 Women today have more options than ever to boost their confidence through modern cosmetic treatments. From simple procedures to more complex surgeries, these treatments help many women feel better about their appearance and themselves overall.
Women today have more options than ever to boost their confidence through modern cosmetic treatments. From simple procedures to more complex surgeries, these treatments help many women feel better about their appearance and themselves overall.
Breast augmentation stands out as one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries, helping women achieve their desired body shape and improve their self-image. This procedure can be life-changing for those who have felt insecure about their bodies, whether due to natural development, changes after pregnancy, or weight fluctuations.
The beauty industry continues to evolve with safer techniques and more natural-looking results. Many women report not just physical changes after treatments like breast augmentation but also improvements in their mental well-being and social confidence, allowing them to focus less on perceived flaws and more on living fully.
Understanding Breast Augmentation
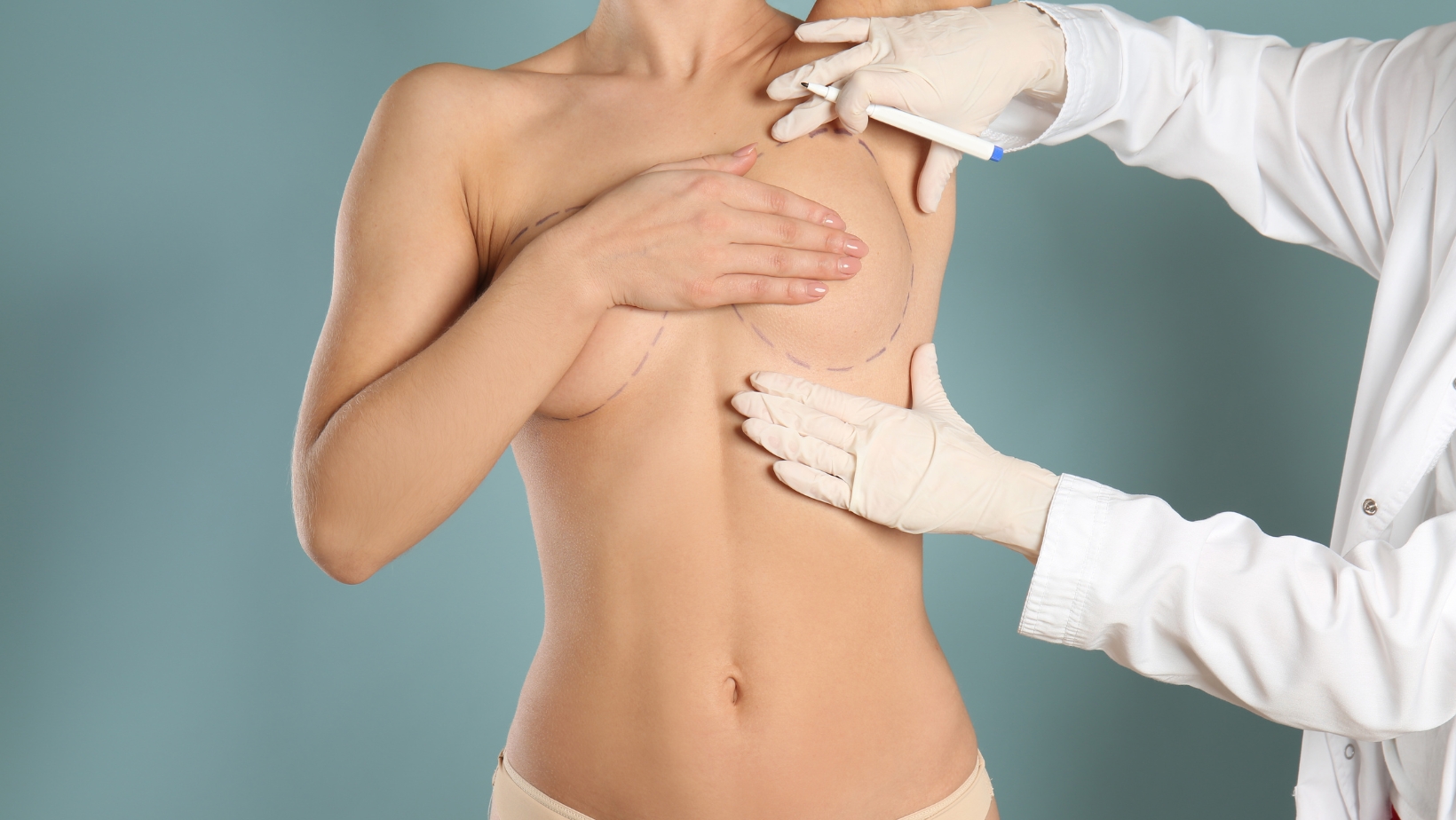
Breast augmentation is a popular cosmetic procedure that enhances breast size and shape through surgical implantation.
This procedure has evolved significantly over the years, offering women various options to achieve their desired aesthetic goals.
Types of Breast Implants
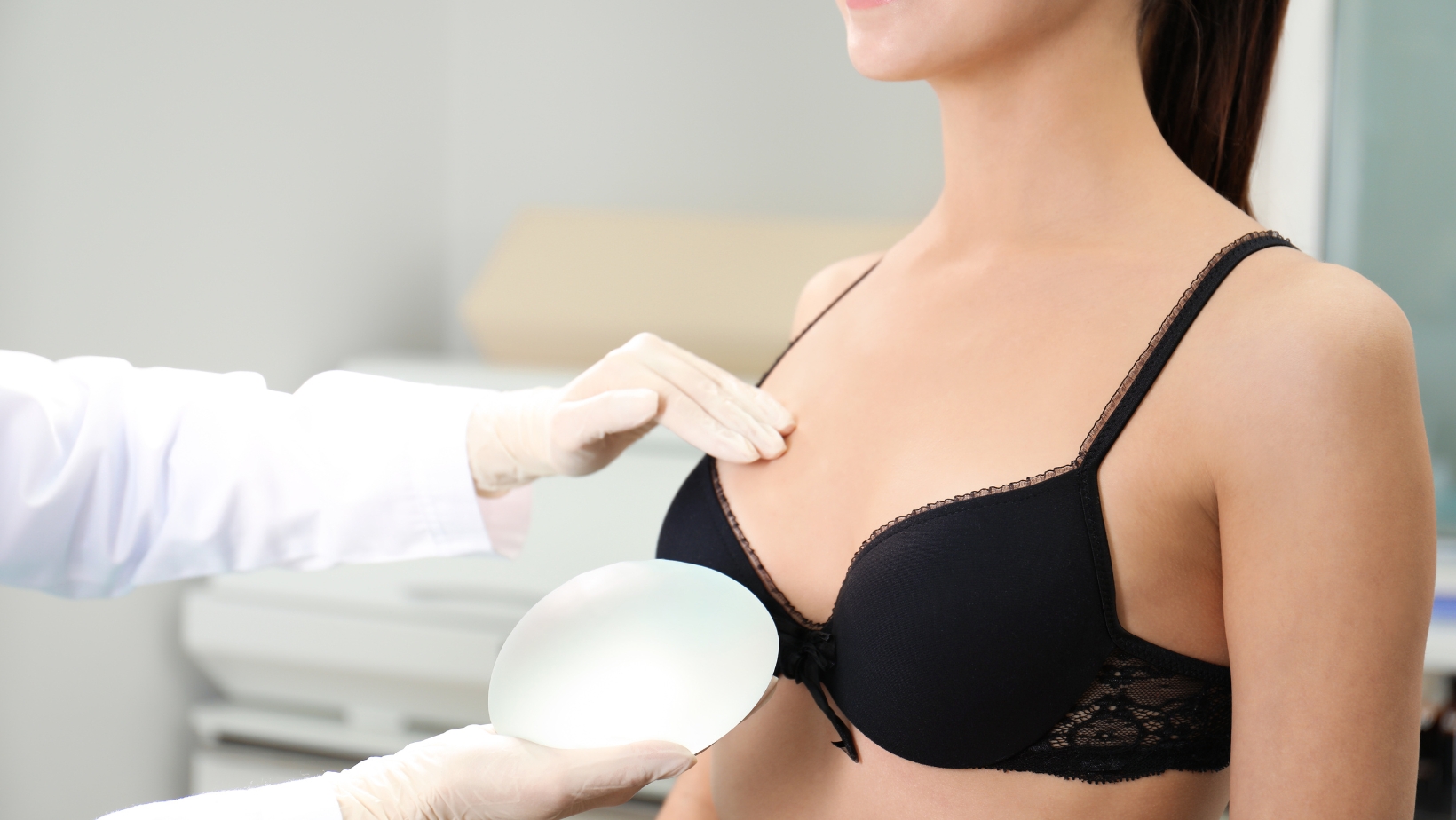
Breast implants come in several varieties, each with unique characteristics suited to different needs. Saline implants contain sterile salt water and provide a uniform shape and firmness. If these implants leak, the body safely absorbs the saline solution.
Silicone implants are filled with silicone gel that feels similar to natural breast tissue. Modern versions use cohesive silicone gel that maintains its shape even if the implant shell breaks. This “gummy bear” consistency reduces concerns about leakage.
Implants also vary in shape. Round implants create a fuller appearance in the upper part of the breast, while anatomical or teardrop-shaped implants mimic the natural breast slope. Implants come in different sizes, projections, and textures to match individual body types and goals.
Surgical Techniques and Considerations
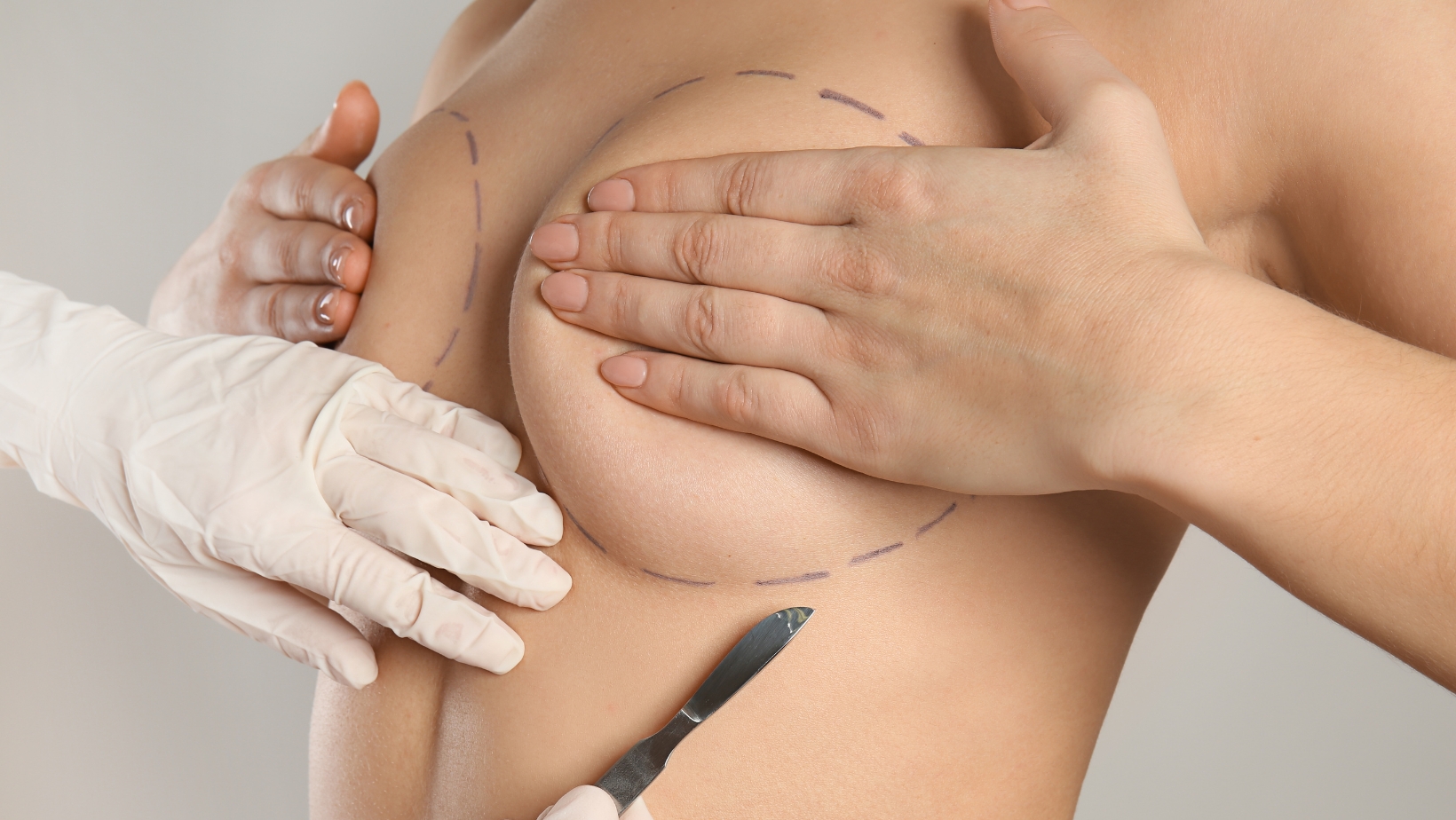
Plastic surgeons typically perform breast augmentation, and the procedure usually takes 1-2 hours under general anesthesia. During the surgery, the surgeon can place incisions in several locations:
- Inframammary (under the breast fold)
- Periareolar (around the nipple)
- Transaxillary (in the armpit)
- Transumbilical (through the navel)
Implant placement options include:
- Subglandular – above the chest muscle, beneath the breast tissue
- Submuscular – partially or completely under the chest muscle
Patients usually need 1-2 weeks to recover from the surgery before returning to normal activities. Expect some swelling and discomfort initially, but these should subside over time as the implants settle and tissues adjust.
Achieving Aesthetic Goals with Breast Enhancement
Breast augmentation can address various aesthetic concerns beyond simply increasing size. The procedure can improve breast symmetry when one breast differs from the other in size or shape. It can also restore volume lost after pregnancy or significant weight loss.
Natural-looking results depend on choosing implants that complement the patient’s body frame and natural breast tissue. Factors like chest width, shoulder width, and existing breast dimensions influence the appropriate implant selection.
During consultation, surgeons help patients visualize potential outcomes through 3D imaging or sizers placed in a special bra. This collaborative process ensures realistic expectations and satisfying results. The goal is enhancement that appears proportionate and harmonious with the patient’s overall physique.
The Journey Towards Recovery and Confidence
Recovery after breast augmentation requires time and patience. The path from surgery to fully enjoying the results involves several stages, with proper care leading to improved confidence and satisfaction.
The Recovery Process
Most women can return to light activities within 24-48 hours after breast augmentation. However, complete recovery typically takes 4-6 weeks. During the first week, patients experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort that gradually improves.
Surgeons usually recommend wearing a special surgical bra to support the healing tissues. Patients should avoid heavy lifting (over 5 pounds) and strenuous exercises for at least 3-4 weeks.
Pain management typically involves prescribed medications for the first few days, then over-the-counter options. Many women report that the discomfort feels more like muscle soreness than sharp pain.

Sleep position matters too. Patients should sleep on their back with their upper body slightly elevated to reduce swelling and pressure on the breasts.
Managing Expectations and Post-Surgery Well-Being
The final results of breast augmentation aren’t immediately visible. Implants need time to “drop and fluff” into their natural position, which can take 3-6 months.
Mental well-being plays a crucial role in recovery. Some women experience temporary emotional fluctuations due to anesthesia effects, pain medications, and adjusting to their new appearance.
Nutrition and hydration significantly impact healing. A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals helps tissues repair faster. Staying hydrated aids in flushing out anesthesia and reducing swelling.
Follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring progress. These visits allow surgeons to check incision healing and implant position and address any concerns.
Addressing Complications: Silent Rupture and More
While serious complications are rare, patients should be aware of potential issues. Capsular contracture—hardening of scar tissue around implants—occurs in about 5-10% of cases and may require additional surgery.
Silent rupture, particularly in silicone implants, can occur without obvious symptoms. The FDA recommends MRI screening 3 years after surgery and every 2 years thereafter to detect these invisible breaks.
Infection risk is highest in the first month. Signs include increased pain, redness, warmth, and fever. Prompt medical attention for these symptoms is essential.
Women with implants can still undergo breast cancer screening, though additional mammogram views or ultrasound may be needed for thorough examination.
Modern implants are designed to last 10-20 years, but they aren’t lifetime devices. Most patients will eventually need implant replacement or removal.